We have recently added increased capabilities for analysis to include pit morphology, pit depth and high magnification photography. Corrosion coupons are usually mounted on fixed and retractable holders and stress coupon racks. See description in Corrosion Coupon Holders section. For pricing please contact EnhanceCo, Inc. Training and Field Services EnhanceCo provides training, installation and other field services upon request. Contact Us.
- Various materials are commonly used:.
- What Do Corrosion Coupons Do??
- CNY - Detection device for corrosion inside pipes - Google Patents;
- pizza huts deals in karachi.
- sky high niles coupon code.
- tesco coupons ireland 2019;
Order Form. Dear visitor, unfortunately online submission form is not supported by Internet Explorer browser. The problems are that these factors do not affect the pipeline equally at all locations and corrosion does not grow at the same rate throughout a pipeline. If operator can identify those corrosion defects which are active or growing, then predictions of future corrosion severity for each and every defect can be made. The existing corrosion mitigation programs are quite effective to combat corrosion problem.
The difficulty is that for various reasons, programs can fail to provide adequate protection in specific, isolated areas. The reasons may include soil conditions, cathodic protection shielding and interference, or inadequate inhibitor concentrations. Any integrity management plan which addresses when to conduct future repairs and when to re-inspect the pipeline has a tendency to make some assumption of corrosion rate, whether explicitly or implicitly, due to insufficient information pertaining to metal loss mechanism.
An estimation of corrosion rates may be applied from engineering judgement based on years of experience and intricate knowledge of a pipeline, or it may be a sophisticated scientific assessment incorporating detailed pipeline data Nesic, A proper and accurate corrosion model can greatly assist engineers in making decisions related to design, operations and control. Available model: Melchers and Jeffrey reported that models for corrosion loss are generally commenced with Tammann in who solved the mathematics for the diffusion of oxygen through the tarnish layers formed on copper, then followed by Booth who then refined the mathematics although this usually is simplified to a corrosion or pit depth c t growth law of the form as follows:.
As reported by Shi and Mahadevan , a seven-stage conceptual model was identified by Goswami and Hoeppner from the onset of corrosion fatigue fracture.
Corrosion Coupon, Injection & Sampling Quill
A three-stage probabilistic model was proposed by Harlow and Wei to predict the corrosion fatigue life as well as a probabilistic model for the growth of corrosion pit induced by constituent particles. The transition model for pitting to corrosion fatigue crack nucleation has been first proposed by Kondo and further discussed by Chen et al. Generally, deterministic and probabilistic models of varying degrees of accuracy are available for various stages of the corrosion fatigue life.
The model that incorporates all the seven stages of corrosion life is proposed by Shi and Mahadevan using a comprehensive probabilistic method. The seven stages consists of pit nucleation, pit growth, transition from pitting to fatigue crack nucleation, short crack growth, transition from short crack to long crack, long crack growth and fracture. To date, empirical model for predicting the growth of external corrosion defects on buried pipelines is hardly available. Most of the established models such as the De Waard et al.
Moreover, the intricacy of physical corrosion models may deter pipeline operator from using it in their maintenance program. There is an immense need for new empirical model capable of estimating the growth rate of external defects under influence of soil properties. For buried gas pipelines, the external corrosion is a great concern than the internal growth due to severe exposure to various condition of soil.
The internal corrosion for buried gas pipelines is less critical because the pipelines are used to transport processed gas or cleaned gas with less impurity. The benefits of the research is to give better understanding on the actual behaviour of corroding steel under exposure to various soil type s and conditions, knowing the most optimum potential for cathodic protection for specific site, reduce the uncertainties in the estimation of corrosion growth, assist the operators in decision making and reduce the overall operating cost.
External corrosion of buried pipelines: Corrosion may act on the pipelines either internally or externally or both. Furthermore, it may be uniform or nearly uniform in nature or localised in extent and severity e. External corrosion is a major factor contributing to the deterioration of buried pipelines; it weakens the pipe wall, which increases the risk of failure Ahammed and Melchers, External corrosion is a function of the interaction between the pipelines and the soil that surrounds it Doyle et al.
The external corrosion of gas transmission pipelines is usually controlled by the application of various polymetric coatings augmented with Cathodic Protection CP Bullard et al. Most common pipeline corrosion protection is done by coating with special material that protects the surface from corrosive elements, such as the type of the soil, moisture, pH, temperature variations and other factors such as resistivity and the presence of sulphate reducing bacteria Alodan and Abdulaleem, ; Bullard et al.
The common types of corrosion that can occur in a buried pipeline are: a pitting corrosion owing to material in-homogeneities, b chloride or sulphate induced stress corrosion cracking, c corrosion by concentration cells in soil arising out of differences in oxygen concentration in the soil adjacent to the pipe at different regions, d microbiologically induced corrosion under anaerobic conditions by sulphate-reducing bacteria SRB and Acid-producing Bacteria APB , e tuberculation because of the build up of corrosion products on the internal pipe surfaces and f stray current corrosion by earth return direct currents.
The metal loss information can be utilised to model the external corrosion as experienced by buried gas pipelines exposed to various soil conditions soil type s, properties and contents or to verify corrosion potential data gained through Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy EIS , for instance. It is of importance to identify the relationship between various soil conditions and the severity of corrosion rate so that the modelling of corrosion dynamic can simulate the actual mechanism as accurate as possible.
The pipeline materials will be exposed to various environmental conditions and continuously monitored to determine the corrosion growth rate on site. Apart from modelling, the measured corrosion growth rate can also be utilised in the probabilistic-based assessment of pipeline integrity. Then, the outcomes of the assessment can be used for determination of inspection intervals and other integrity monitoring programmes.
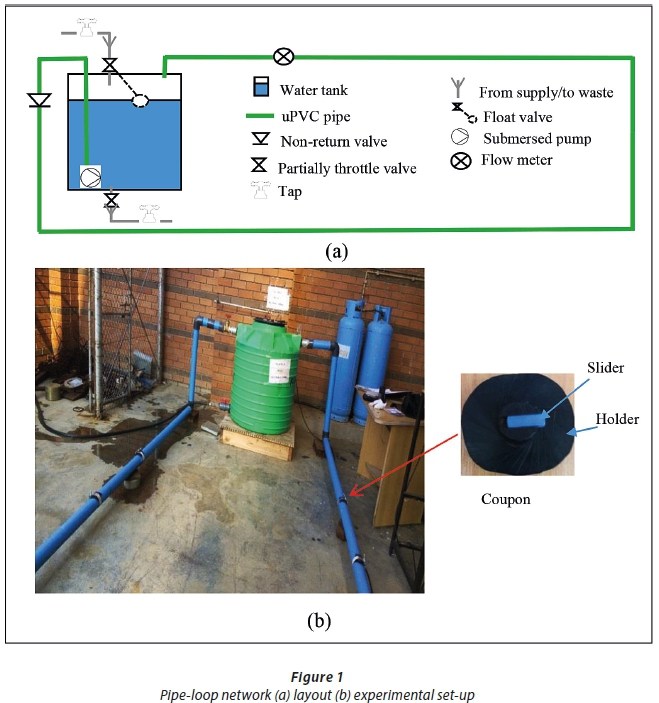
The study focuses on the relationship of soil condition and degree of exposure to the external growth of corrosion defects. The available inspection data and previous maintenance record will be used to determine the exact location for soil sampling based on the severity of corrosion attack. The investigated pipelines throughout the research are made of steel from various grades and sizes.
Soil corrosion factors: Soil has many different meanings depending on the field of study. To a geotechnical engineer, soil has much broader meaning and can include not only agronomic material, but also broken-up fragments of rock, volcanic ash, alluvium, Aeolian sand, glacial material, and any other residual or transported product of rock weathering Day, Its physical and chemical characteristics are different from sea-bed sediment soil, salina soil and tideland soil.
Soil is a complex material; a porous heterogeneous and discontinuous environment constituted by mineral or organic solid phase, water liquid phase and airs other gas phase Rim-Rukeh and Awatefe, Ferreira et al. According to Ferreira et al. The study of the soil as a corrosive environment is necessary due to the large number of buried pipelines, tank and other structures, as their deterioration can represent a real economical and environmental problem throughout the years.
There are several parameters that can affect the corrosivity of a soil such as resistivity, pH, redox potential, moisture content , type of soil, chloride and others. In agreement with the parameters cited above, Fitzgerald studied shows the corrosivity of the soil influenced by oxygen content, dissolved salts, pH, elements that form acids, concentration of chloride, sulphide and sulphate, resistivity, total acidity, redox potential and others, depending on specific application. The specific test for external corrosion due to soil corrosivity will be discussed in the next section. The research duration is designed for 36 months period divided into several stages as shown in Fig.
The project will commences with a 6 month of initial data collection, site visits and establishment of research method. This will be followed by another 6 months of soil sampling, experimental set-ups, preparation of testing materials and initial experiments.
Various types and styles of coupons are available:
Upon completion of the activities in Stage 1, corrosion experimental studies and simulation of predicted corrosion growth rates will be carried out in Stage 2 and followed by Stage 3 for a period of twelve months each. The sequences of research activities are planned as shown in Fig. An overview of test conducted in this study is shown in Fig. Laboratory test may be classified conveniently as follows:. Laboratory studies have shown that electrochemistry-based corrosion rate probes can be used to monitor the corrosion of steel in soils Shreir, Corrosion rates were shown to have a good agreement with gravimetric weight loss measurements and were also sensitive to changes in soil moisture and salt content.
Corrosion coupons testing | Pipeline installation & analysis | EnhanceCo
Others have shown that electrical resistivity probes can be used to monitor the effectiveness of cathodic protection of pipelines Bullard et al. According to previous researchers there are several types of instrument, parameters and methods can be used in corrosion testing. Laboratory-based corrosion tests fall into the following categories comprises immersion test, simulated atmosphere tests, electrochemical tests and environmentally aggressive tests Fig. All of these are accelerated tests by design and therefore must be carefully carried out.
Soil sample collection: Soil sample for this study will be randomly collected from different sites. At each of the selected site, samples will be collected by digging a hole of 1 m deep. Soil samples will be collected from each sites and kept in polyethylene bags before sent to the laboratory immediately for further soil analysis.
Both wet sieving and sedimentation analysis are used to get full particle distribution analysis of the sample under investigation. The parameters analysed comprises moisture content, liquid limit, plastic limit, plasticity index, shrinkage limit and particle size distribution. Moisture content of the soil samples can be ascertained using the weight loss technique according to BS BSI, a. The weight difference between the sample before and after evaporation is regarded as the moisture content. The soil samples are saturated with distilled water and placed in different rectangular boxes with an open top.
The boxes are filled to the top with soil. The value of resistivity can be evaluated using Eq. Temperature is an important parameter in the investigation of soil corrosivity because it can modify the interactions between the metal and the soil conditions Rim-Rukeh and Awatefe, Soil resistivity is a measure of the ability of a soil to conduct an electrical current Rim-Rukeh and Awatefe, American Standard of Material and Testing, b.
The resistivity of the soil is determined by moisture content and the concentrations of the different ions and their mobility.